Today, in an era when our lives are interconnected through digital technology, the importance of information security in federal agencies cannot be overstated. The risks, ranging from data breaches to cyber terrorism, demand robust protective measures. This makes the role of guidance in establishing controls absolutely essential.
The purpose of this article is to elucidate the frameworks and guidelines that shape federal information security controls. It will present an overview of the subject matter, dive into the NIST Framework, and touch upon Federal Information Processing Standards.
Overview of Federal Information Security Controls

Information Security Controls are safeguards or countermeasures employed to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. They are pivotal in managing the risks related to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of data.
The significance of federal information security controls stretches far and wide. These measures not only ensure the secure operation of federal agencies but also safeguard the data of millions of citizens. In fact, the very impact on national security and public interest is profound.
Importance of Federal Information Security Controls |
| Protecting the operational integrity of federal agencies |
| Safeguarding the data of millions of citizens |
| Ensuring national security |
| Promoting public interest |
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Framework
NIST, a component of the Department of Commerce, is a key entity that formulates standards, guidelines, and minimum requirements for providing adequate information security.
NIST Special Publications |
Purpose |
| SP 800-53 | Security and Privacy Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations |
| SP 800-37 | Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and Organizations |
| SP 800-171 | Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information in Non-federal Systems and Organizations |
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
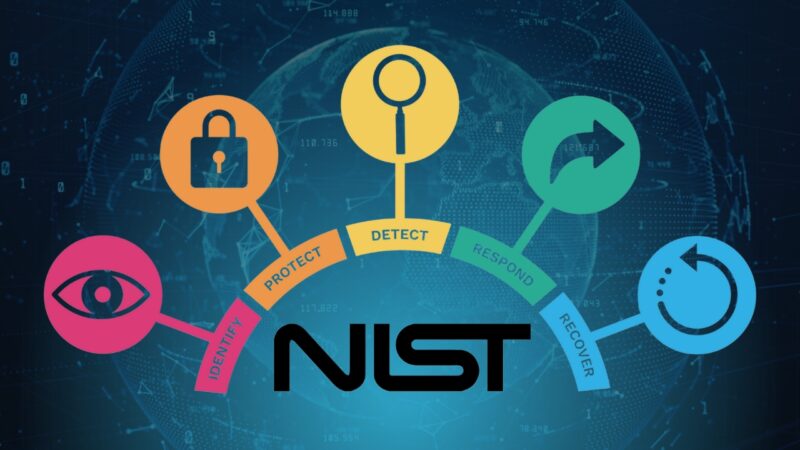
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is another key pillar of federal information security. It introduces core functions and implementation tiers and fosters collaboration between the public and private sectors. This allows for a unified approach to managing and reducing cybersecurity risk in a cost-effective way.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Components |
Description |
| Core Functions | Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover |
| Implementation Tiers | Partial, Risk Informed, Repeatable, Adaptive |
| Collaboration | Public and Private Sector Cooperation |
Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS)
FIPS are developed by NIST for use in computer systems by all non-military government agencies and by government contractors. These standards underline the federal government’s commitment to information security and its role as an exemplar of best practices.
FIPS Publications for Information Security
Various FIPS publications detail specific protocols for different aspects of information security
FIPS Publications |
Purpose |
| FIPS 199 | Standards for Security Categorization of Federal and Information Systems |
| FIPS 200 | Minimum Security Requirements for Federal and Information Systems |
| FIPS 140-2 | Security Requirements for Cryptographic Modules |
Federal Laws, Regulations, and Directives

The legal foundation of information security is built upon several key pieces of legislation and directives from the executive branch.
Federal Laws and Regulations |
Purpose |
| Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) | Development and Implementation of an Enterprise-Wide Information Security Program |
| Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) | Standardized Approach to Security for Cloud Products and Services |
| Executive Order 13800 | Strengthening Cybersecurity of Federal Networks and Critical Infrastructure |
| Presidential Policy Directive 21 | Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience |
Department of Defense (DoD) Information Security Guidance
The DoD has its own set of security regulations in place, further bolstering the nation’s information security infrastructure.
| DoD Security Guidance | Purpose |
| DoD Directive 8500.01 | Guidelines for Managing Risk to DoD Information |
| DoD Instruction 8510.01 | Establishing a Risk Management Framework for DoD IT |
| NIST SP 800-171 | Protection of Controlled Unclassified Information in Non-DoD Systems and Organizations |
The Role of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
The OMB plays a pivotal role in shaping federal information security policies and procedures.
| OMB Guidance | Purpose |
| Circular A-130 | Policy for the Management of Federal Information Resources |
| OMB Memorandums | Timely Guidance to Agencies on Information Security Issues |
Collaboration with the Department of Homeland Security (DHS)

The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is a critical partner in enhancing the nation’s information security through its Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) guidance.
| DHS Collaboration | Purpose |
| CISA Guidance | Resources, Tools, and Best Practices for Cybersecurity Management |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Information Sharing and Incident Response to Address Cyber Threats |
Continuous Monitoring and Compliance
Continuous monitoring in maintaining a robust cybersecurity helps agencies to keep a vigilant eye on their cybersecurity landscape and promptly respond to any potential threats.
Continuous Monitoring and Compliance |
Description |
| Importance of Continuous Monitoring | Real-time insights into security posture |
| Compliance Reporting and Auditing | Ensuring implementation and functionality of security controls |
| Challenges and Benefits | Balancing resource intensity and complexity with real-time detection and mitigation of threats |
Fun Fact
Did you know that the Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) was originally called the E-Government Act of 2002? It was renamed in 2014 to better reflect its purpose!
FAQ

What is the role of the NIST in federal information security?
It establishes and updates standards, guidelines, and methodologies to help federal agencies and contractors improve their cybersecurity posture. NIST also develops frameworks, such as the Cybersecurity Framework, to provide strategic guidance on managing cybersecurity risk.
Why is FIPS important in federal information security?
They are federal government standards that provide parameters for various areas including encryption algorithms, security categorization, and minimum security requirements for information systems.
How does the DoD enhance federal information security?
The Department of Defense (DoD) enhances federal information security through its own set of stringent regulations and guidelines. also leverages NIST standards in its contracts to ensure the security of its information systems.
What is the impact of federal information security controls on national security?
They protect the government’s critical infrastructure and sensitive data from cyber threats, thereby ensuring the continuity of government functions. Furthermore, they safeguard the privacy of citizens by protecting personally identifiable information, enhancing the public’s trust in government services.
Understanding the frameworks that guide federal information security is crucial, especially considering the growing number of cyber attacks each day, which pose significant threats to sensitive data.”
Conclusion
Federal information security controls are an integral part of our national security and public interest. With the guidance continuously evolving to keep up with emerging threats, it is vital to maintain vigilance and adaptability. Remember, information security is not a one-time task but an ongoing process!

